A brief introduction to digital file formats used in the Print industry and Web publishing.
File Format for Printing (PDF)

The myth that “print” is dead…
Despite living in a screen centered world, the print industry is chugging along just fine! We still buy books, magazines, products with printed visuals on them, and we interact with advertisement everywhere in the physical world.
CMYK color
Projects for print should be created in the CMYK color space (or process color, or four color) and saved as .PDF file format.
The PDF (portable document format) is a versatile file format, the standard for sharing files across different platforms, and for printing on commercial and portable printers.
print publishing:
- Microsoft Word documents
- Newsletters
- Annual reports
- Artworks created in Photoshop, Illustrator, Gimp, Inkscape, Procreate or any digital media app.
- Posters
- Books, magazines, comic books
- Banners, Vinyl designs that can be applied to glass windows, for example.
RGB Color
When creating graphics for screen publishing, you typically work in the RGB color space and the file format you choose depends on the type of image.
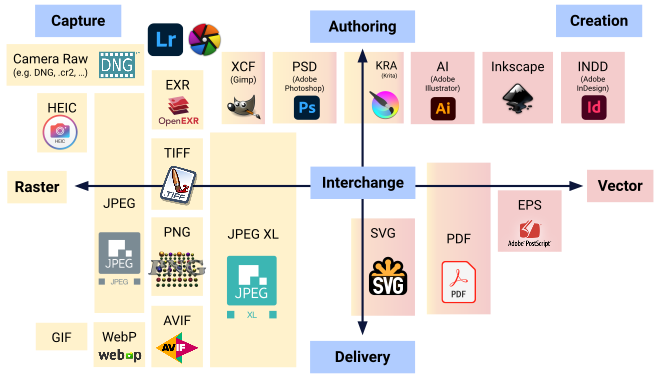
Raster File Formats (.JPEG, .PNG, .GIF, .TIFF, .PSD)
Raster for Screens
Typically, JPEG for photos and pictures of colorful art, and PNG for logos, simple graphics such as logo, typography, and complex digital art. Raster file format is ideal for photos and images such as digital art created in programs like Photoshop.
Raster for Print
Raster images destined for print should be created in the CMYK color space (or process color, or four color) and saved as .PDF file format.
Images used in print projects, such as newsletters, brochures, should be saved as high resolution TIFF file format, at a 300 ppi (pixels per inch) resolution.
.JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group)
- .JPEG is a lossy file format that is the best used for photos and photos of fine art images.
.PNG (Portable Network Graphic), also pronounced “ping”
- PNG is best when used for images that are graphical nature such as logos, cartoons, illustrations, graphic design projects in general. Also, PNG is also suitable for digital paintings created in applications such as Photoshop, Procreate, Fresco. PNG format uses lossless compression, so the file size could be larger than JPEG, depending on the image complexity and dimensions. PNG file format also supports alpha channel, for posting an image with a transparent background or no background around the subject.
.GIF (Graphics Interchange Format)
- Before the PNG file format became a web standard, GIF file format was widely used for graphics for screen publishing. Also to this day, GIF file format is widely popular since it supports animation. “The Graphics Interchange Format (GIF; / ɡ ɪ f / GHIF or / dʒ ɪ f / JIF, see pronunciation) is a bitmap image format that was developed by a team at the online services provider CompuServe led by American computer scientist Steve Wilhite and released on June 15, 1987.” wikipedia
.TIFF (Tag Image File Format)
- The most widely used file format for archival of high resolution images. Tiff is not a web file format and it should not be used for screen publishing, since it is not supported. Tiffs can be opened by any application that handles graphics: you don’t need proprietary software to open and edit Tiff images and it is supported by all operating systems, Linux, Mac Os, and Windows. Tiff is widely used in the printing industry and by photographers and artists to store high resolution versions of their works.
.PSD (Photoshop Document)
- PSD is the Photoshop authoring or proprietary file format for raster images. You should always save a PSD version of any work you create in Photoshop, even if you saved a separate version as a different file format for web or for print.
Screen publishing
When posting an image on Instagram, on a website, or on the web in general, you need to export a compressed and properly sized version of the photo.
- Uploading photos to social media, such as Facebook, Twitter, etc.
- Placing images on webpages
- Images for video projects
- Images for powerpoint-like presentations
Vector File Formats ( .SVG, .AI, .PDF, .EPS )
SVG File format
Scalable Vector Graphic, is the open source vector file type. It can be scaled indefinitely without loss of resolution. Read more about this file format on Adding Vector Graphics to the Web. Adobe Illustrator can save to SVG format. Also SVG is the file format used by Inkscape, an open source vector graphics program.
AI File format
The Adobe Illustrator file format, typically used for creating vector graphics such as logos, icons, and for creating vector versions of art or photos.
EPS File format
Encapsulated PostScript format used to be widely used as a final file format for printing, but it doesn’t support transparency as well as some of the other SVG and AI formats.
PDF File Format
Portable Document Format, the industry standard for print files, and for exchanging documents. Every document that needs to be attached to an email, viewed and read by people other than the author, should be saved as PDF. PDF files can be edited by Adobe Acrobat.
File Dimension vs Resolution when preparing images for web.
Resolution
When preparing images for the web, resolution takes a back seat to dimension (in pixels).
All files for web should be 72 ppi resolution. Actually, images saved with 72 ppi look great as long as the dimension (actual size in pixels) is planned accordingly.
Only documents for print need to be high resolution, such as images included in a print document. All images used in a document for print should be 300 pixels per inch and should be saved as TIFFs.
High resolution images for the web do not improve image quality, when viewed on an electronic device, and will slow down the download times since the file size (weight) is larger.
dimension (in pixels)

The image above was saved as a JPEG, and the dimensions at 500 by 375 pixels. It is a relatively small image in dimension since it is less wide than this paragraph. It is 250KB in size.
The important consideration for web publishing is the dimension in pixels. You should use large dimension images for hero banners, for occupying large areas of a web page.
Depending on the size of the web page and the target audience, even for a banner, an image shouldn’t be much bigger than 2000 pixels.
If you need the same banner image to be placed elsewhere, as a small thumbnail, you should upload a smaller version that banner image.
Visitors will stay longer on your website, if images load properly, they will be able to engage with the images without having to wait for them to download. When images aren’t properly optimized and take a long time to preview, you’ll end up loosing traffic.
The highest the resolution, the highest the pixel dimension of the image. For instance, 4K resolution means 4000 pixels. An image posted on social media does not need to be 4k resolution, since it will be viewed on a relatively small screen.
Multimedia File Formats ( .MP3, .AIF, .WAV .MP4, .MOV, .AVI )
When you create digital projects with programs such as Photoshop and Illustrator you have to save those images as JPEGs, PNGs, PDFs, depending on the publishing context (print or web).
The same applies when working with multimedia applications such as Adobe Audition (.AEP) and Adobe Premiere (.PRPROJ). Once you finish an Audition project, you will save a file as non-compressed audio file .WAV or .AIFF. When publishing an audio file for the web, .MP3 is one of the widely used audio formats.
Once you complete a video editing project in Premiere Pro, a typical workflow is to save a version of the project as a non-compressed movie file, .MOV or .AVI. To place a video on the web, you will export to the .MP4 file format.
Professional Cameras and Phone Cameras
Some cameras and phone cameras use .JPEG as the default file format, and you can specify the default resolution ( low, medium, high or maximum ).
Ideally, the camera should be using the maximum resolution setting the device is able to handle. Those images should be saved in your cloud, or computer hard drive for permanent archival, preferably as a copy in the .TIFF file format.
When you work with professional DSLRs ( digital single-lens reflex ) cameras such as Nikon (uses .NEF raw file format) or Canon (.CRW raw file format), photos are initially created in RAW format.
The RAW format allows for the highest possible resolution and to capture the most detail when taking photos.
RAW format photos need to be processed by software like Photoshop, saved as a separate raster format like JPEG or TIFF prior to publishing or for working with those images in a graphics program.
Examples
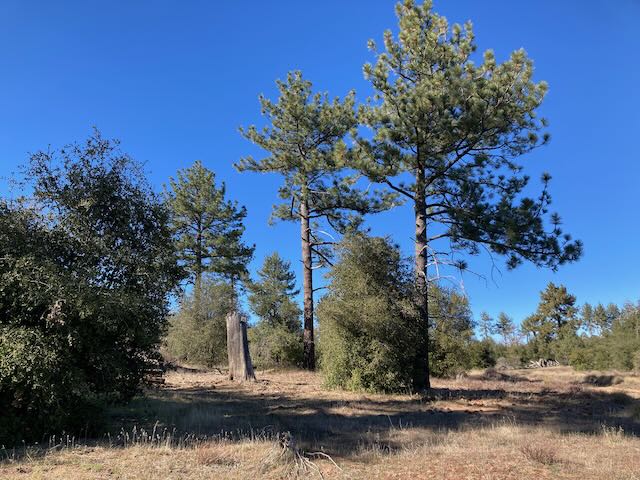
Example using JPEG file format (RASTER IMAGE)
The image on the right, is a photo of a landscape, it is a raster image, saved as a JPEG, using medium, compression and 600 pixels for the width (dimension). The original photo is 3000px wide and it is too big to fit in this page and it is too large (file size) to download effectively.

Example using PNG file format (RASTER IMAGE*)

This logo was created in Adobe Illustrator, so it is vector art, that was then saved as a PNG. The file has an alpha channel and the X is actually transparent, but it looks white because it is embedded on a white web page. The file size is only 3k, and the dimension is 209 by 141 pixels.
*The “THE EXIS HOTEL” logo was created in Adobe Illustrator, and the original authoring file is a vector (.AI) file. To place the image on this web page, it was exported as a .PNG (a raster image).
Additional Resources
Image file type and format guide (External Website)
From the W3 Schools, information on GIFs VS PNGs
What is a vector file and how to use them (External Website, Adobe)